CBDC Characteristics
1. CBDC Classification
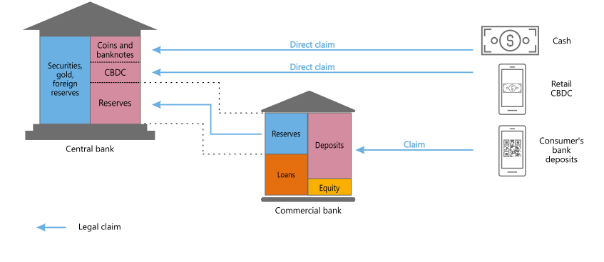
Central banks play a key role in wholesale and retail payment systems. On the one hand, commercial banks deposit reserve funds with the central bank to ensure that customers withdraw deposits and fund settlement needs; on the other hand, the central bank issues cash to the public to meet daily payment needs. Central banks play an irreplaceable role in ensuring security, integrity, efficiency and inclusiveness in the payment field.
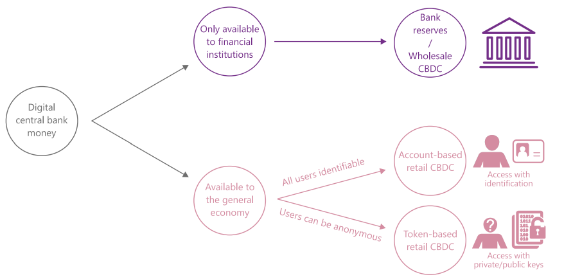
a. Wholesale CBDC
It is mainly used by financial institutions and is established under the traditional two-tier monetary system, that is, the central bank establishes a payment system, and then the payment system participants provide CBDC to the public. The central bank provides accounts to commercial banks and other payment service providers and settles through the central bank's balance sheet. Wholesale CBDC has two major advantages: First, it is used for payments between financial institutions, including digital assets and cross-border payments. The operation of wholesale CBDC is very similar to central bank deposit reserves: it settles by debiting the bank accounts that owe net debts to other parts of the system and crediting the bank accounts that have net claims on the system. Second, it enhances the cash-currency pairing mechanism in RTGS systems, requiring that a payment can only be settled on the condition that another payment is delivered or an asset is delivered.
b. Retail CBDC
The central bank directly issues CBDC to the public, which optimizes the traditional monetary system and does not bring credit risk to banks. In comparison, other forms of intermediate participants may interrupt payments due to temporary lack of liquidity or bankruptcy, although collateral and other security measures have greatly reduced this risk. Retail CBDC can completely avoid such risks. There are two forms of retail CBDC: one is a cash-based design, namely key access and anonymous payment. Individual users can access CBDC using a private key password and a digital signature without personal identity verification. The second is an identity verification design, which establishes a digital identity and account access, and a reasonably designed payment authentication process can achieve controllable anonymity while protecting privacy.
2. The differences and similarities between the CBDC system and the mainstream FPS (Fast Payment System)
a. Similarities between CBDC and FPS
First, promote payment service innovation, enable payment service providers to compete to develop interfaces to complete payments on various media or channels, such as prepayment cards, smartphones and other dedicated access devices, to save costs and promote the universality and inclusiveness of payments. Second, well-designed CBDC and FPS can promote payment data governance. The central bank can establish a digital identity identification mechanism, use digital signatures to effectively protect personal information of each participant, transfer data control from private payment service providers to users, and gradually break the monopoly of large payment service providers over user data.
b. The main differences between CBDC and FPS
There are differences in the operating architecture. The FPS adopts a two-tier architecture. The retail recipient receives the settlement funds immediately, but the wholesale settlement may be delayed because the intermediate party may settle funds during the payment time difference. This delay means that there is a short-term credit relationship between the two parties to the transaction, and the risk exposure continues to accumulate during the delay, generating potential credit risk. The institutional guarantee mechanism designed by the central bank can provide full or partial guarantees for such exposure. CBDC eliminates transaction intermediaries. After a terminal user issues a payment instruction, the central bank can directly transfer it to another terminal user and settle it in real time, realizing point-to-point payment, eliminating intermediate credit demand, and simplifying the monetary system architecture. In addition, CBDC can also maintain the advantages of traditional legal tender (cash), that is, to establish a tangible link between the public and the central bank, and provide new robust monetary policy tools. The issuance of CBDC by central banks of various countries depends on the efficiency of its traditional payment system, economic development level, legal framework, user preferences and ultimate goals. Considerations of payment security and financial stability tend to be more important in developed economies. Regardless of the ultimate goal, controlling data governance and regulating the competitive landscape under the CBDC system has become a key factor in the central bank's relevant decision making.

